Bed Shear Stress

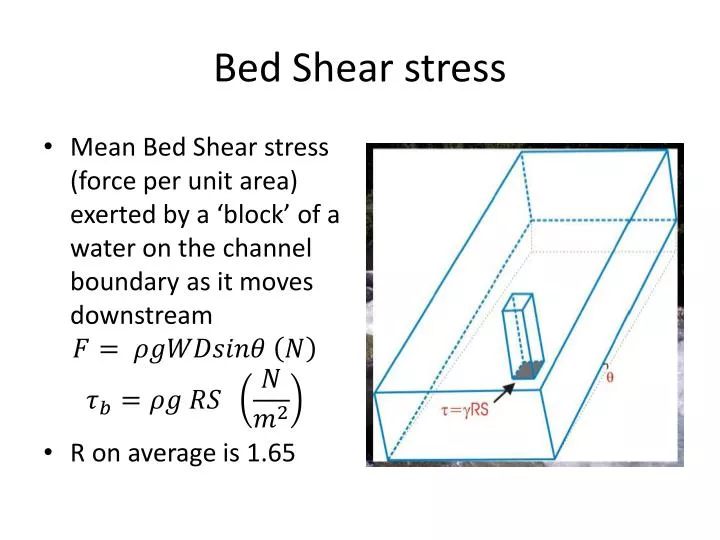
Bed shear stress is an essential parameter in the description of flow motion and sediment transport.
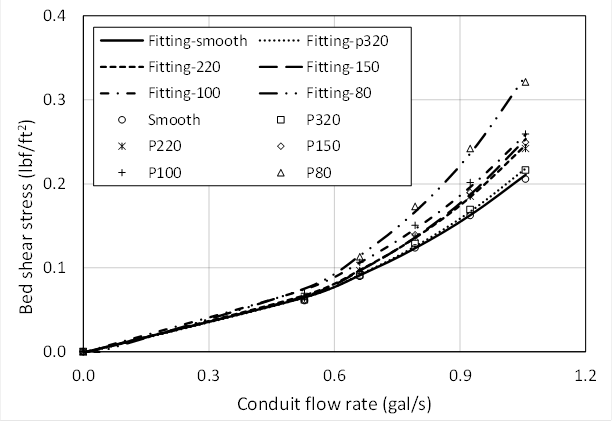
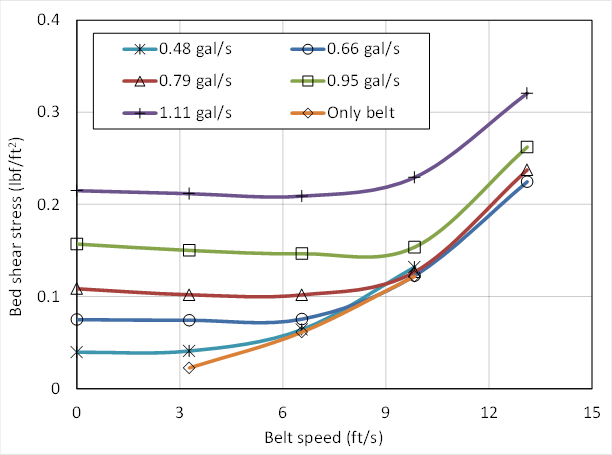
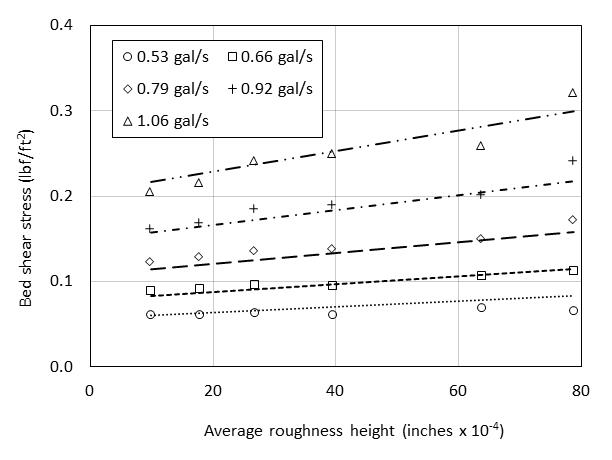
Bed shear stress. In relation to the bed shear stress values shown in Fig. Thompson et al 2004 the production of turbulence in stem wakes can enhance near-bed momentumtransferandincreasetherateofsedimententrainment Nezu and Onitsuka 2001. Several methods exist to estimate the bed shear stress in bare channels without vegetation but most of these are not appropriate for vegetated channels due to the impact of vegetation on the velocity profile and turbulence production.
The partitioning of shear between stems and the bed can reduce bed shear stress Lopez and Garcia 1998. Shear stress is calculated as. Eg the weight of an earth-filled dam or dike may cause the subsoil to collapse like a small landslide.
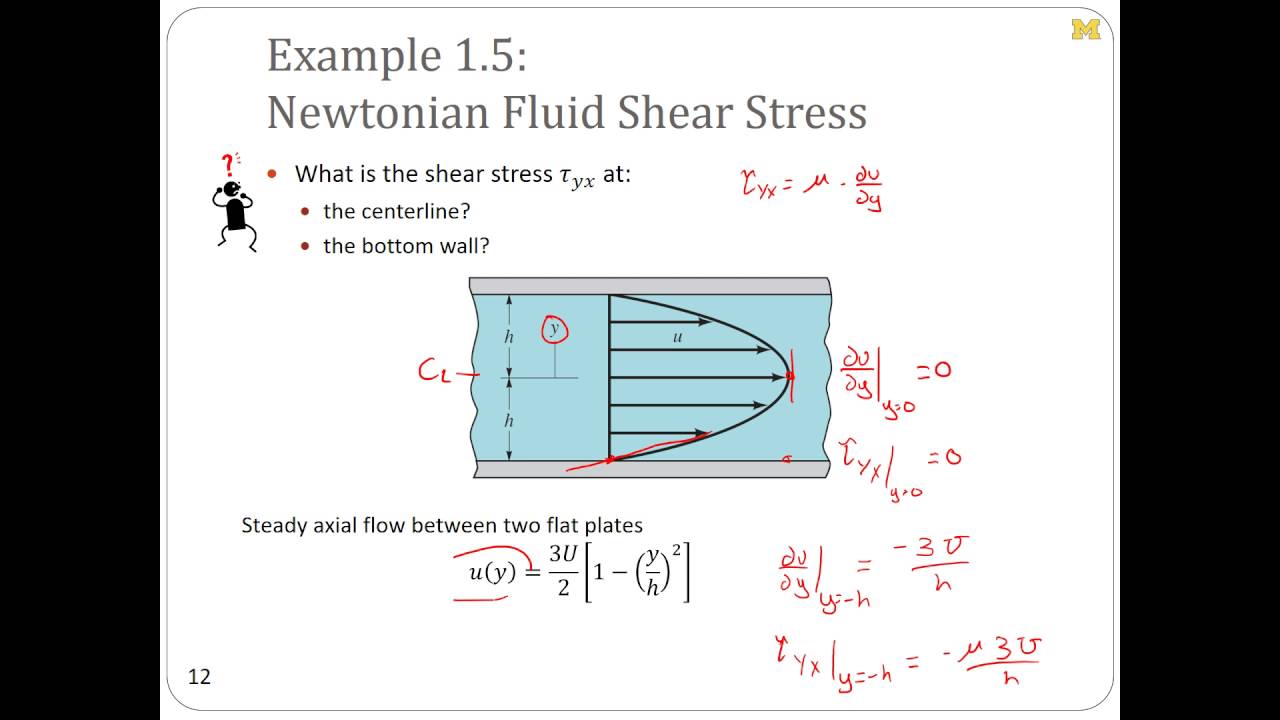
Im not intending to bring anything new but rather to bring together established theories and concepts into a coherent whole that could be of use to engineers designing channel linings. Shear Stress t is a measure of the force of friction from a fluid acting on a body in the path of that fluid. Bed shear stress concept and description.
Bed shear stress is a critical parameter in sediment dynamics on tidal flats especially in the calculation of erosion rates Friedrichs et al 2000 Friedrichs and Wright 2004 Wang et al 2013 and the total bed shear stress is the combined contributions from waves and currents. Dividing the shear flow by the thickness of a given portion of the semi-monocoque structure yields the shear stress. Shear forces exerted on.
Stresses in tidal boundary layer from acoustic doppler velocimeter data Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 126 399-406. 1 from the tip we note that this value corresponds to the impact force of the fluid front hitting a row of roughness elements of height λ and spacing λ. The lack of near-bed measurements is a critical loss of information which may affect bed shear stress estimates.
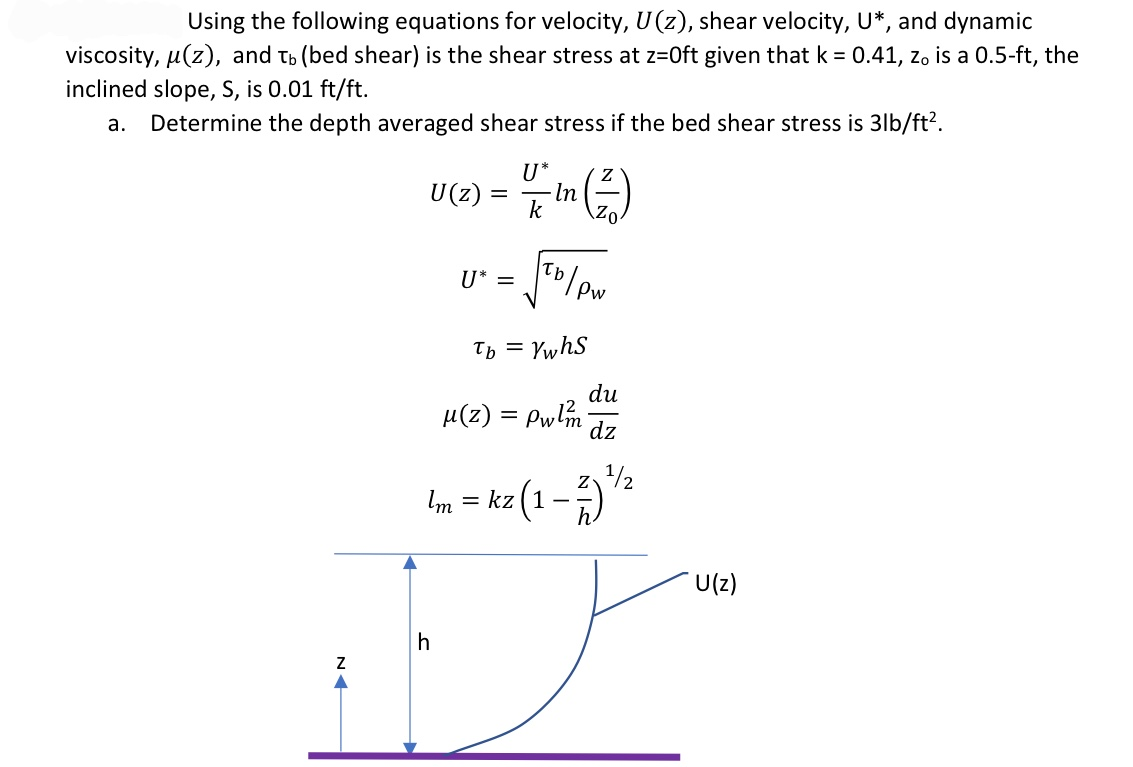
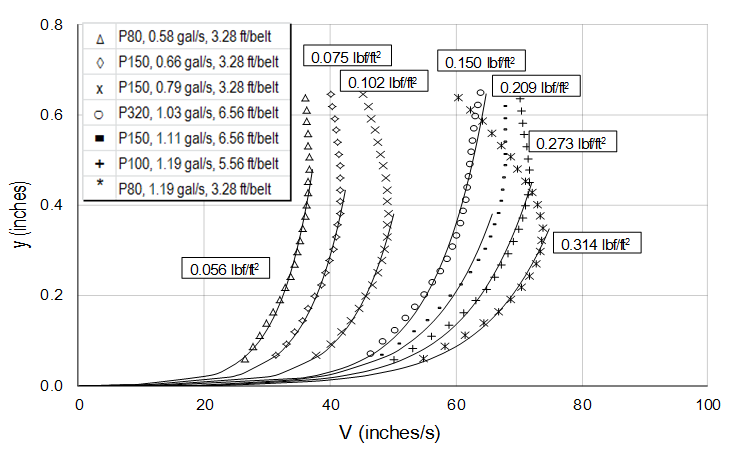
In bare-bed channels the bed shear stress can be estimated using several methods such as fitting the mean velocity profile based on a logarithmic Law of the Wall Figure 1a by the water surface slope method which relies on a momentum balance by extrapolating near-bed turbulent stress and using the empirical. The bed shear stress is governed by the thickness of the viscous layer H v holds over most of the viscous layer except very close to the bed z zu ν 5 with u the friction velocity and ν the kinematic viscosity where the viscous stress is constant Kundu et al 2012. Some researchers have estimated the bed shear stress by subtracting the vegetative drag from the potential forcing Jordanova and James 2003.